How to Measure the Angle of Incidence and Reflection
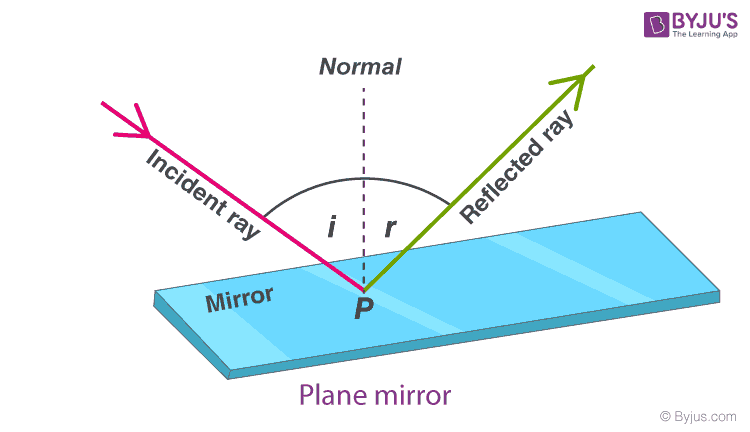
The angle between the incident ray and an imaginary perpendicular line drawn to the surface of the mirror is called the angle of incidence. Angle of incidence.

Angle Of Incidence Definition Formula Diagram Examples
In other words when light comes into.

. SinIIncident velocity SinRreflection velocity. Therefore the angle of incidence is 90-1080. The angle that the incident ray makes with the normal line is referred to as the angle of incidence.
Refraction and angle of incidence. Or may be well be but only in the case of flat objects. The angle of incidence is the angle between a ray of light which hits the surface and the normal line.
The angle between the reflected ray and the perpendicular is called the angle of reflection. The angle of reflection theta_r of a ray or beam is the angle measured from the reflected ray to the surface normal. According to the law of reflection the waves angle of reflection is equal to the waves angle of incidence.
Therefore the angle of reflection is 80. Indicate the colors of the incoming and the outgoing rays and mark them with arrows in the appropriate directions. The following should help you to remember which is the incident ray.
According to the law of reflection light is always reflected at the same angle that it arrives at a surface. From the law of reflection theta_itheta_r where theta_i is the angle of incidence. A beam of light reflecting off a mirror attached to an angle scale proves that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
When a ray of light is incident at normal incidence at right angles to the surface between two optical materials the ray travels in a straight line. They are the angles made by the incident ray and the reflected ray with the line perpendicular to the reflecting surface at the point of reflection. R the angle of refraction.
Method Set up the ray box and slit so that a narrow bright ray of light is produced. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection at a movement against an obstacle and a reflection or rebound there. May be by measuring the angle horizontally we wont be able to explain those phenomenon so neatly.
Shine the colored rays at an angle to the plane mirror. N r the index in the refracting medium Image will be Updated Soon The Angle of Incidence and Angle of Reflection. According to this law fractextsin itextsin r fracn_rn_i Here i the angle of incidence.
Angle of incidence and angle of refraction. From the law of reflection we know that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Here the angles can be calculated for obstacles in a certain angle to the observer.
Disc 21-20 44 sec Back. Place the rectangular glass block on a sheet of white paper and draw around it carefully with a pencil. θ r θ i.
The angle of incidence is not the only angle so defined. The ray of light is called the incident ray. Remove the glass block.
θ r θ i. Theta_r is measured between the ray and a line normal to the surface that intersects the surface at the same point as the ray. It is given that the light ray is making 10 with the surface.
The reflected light will make an angle of reflection that is measured from the reflected beam to the normal and light that is not reflected but continues into the second material will make an angle of refraction with respect to the normal. Angle of incidence and reflection β. The law of reflection tells you that the angle at which the light hits the surface angle of incidence will be equal to the angle at which it bounces away from the surface angle of.
The angle of incidence and angle of refraction are denoted by the following symbols. How do you measure the angles of incidence and reflection. The law of reflection states that when a ray of light reflects off a surface the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
The law of reflection is illustrated in Figure 15 which also shows how the angle of incidence and angle of reflection are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the light ray strikes. The obstacle can be something like a bar or when referring to light a mirror. Similarly the angle that the refracted ray makes with the normal line is referred to as the angle of refraction.
Angle of Incidence θi Angle of Reflection θr. These angles will be discussed later in this lesson. Hence the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
The Law of Sines is he relationship between the incidence angle and the reflection angle. I think we measure the angle with respect to the normal because by doing so we can explain many phenomenon that happens in the nature due to reflection and refraction of light. When the light gets reflected from a plane surface it selects the shortest path.
We know that the normal to the surface is always 90. N i the index in the incident medium. The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence or.
Use the protractor to draw a normal approximately 13 of. This law applies to curved. Mark the position of the surface of the plane mirror and trace the incident and reflected rays.
Visit our help center article on working with legacy web pages and content for more information. We can find the angle of incidence by using Snells Law.
Angle Of Incidence Definition Formula Diagram Examples

Pyhsics 7 3 3 4 Determining The Angle Between An Incident Ray And A Reflected Ray Youtube

Question Video Reflection Nagwa
Pyhsics 7 3 3 4 Determining The Angle Between An Incident Ray And A Reflected Ray Youtube
No comments for "How to Measure the Angle of Incidence and Reflection"
Post a Comment