Best Describes the Process of Fluorescence
Excitation of a fluorophore through the absorption of light energy. Fluorescence occurs when electrons go back from a singlet excited state to the ground state.
Fluorescence Microscopy Basic Concepts In Fluorescence Olympus Ls
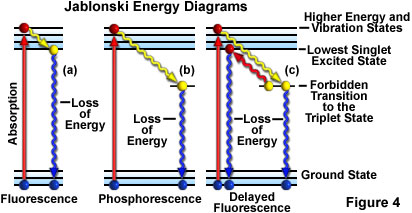
The process of phosphorescence occurs in a manner similar to fluorescence but with a much longer excited state lifetime.
. - A photon of light is then released so electron can return to its original energy state. By spontaneous emission of a photon. The structu of 4- depict a new e under color brightness etc Draw structure to the neutral acidic and basic conditions plus an appropriate resonance chromophore likely responsible for its absorbance.
How does fluorescence occur. The simple kind of fluorescence is by dilute atomic vapors. The vibrational relaxation of any electronic state is always much faster than photon emission.
When chlorophyll is extracted in solution and a bright red or blue light is shown on it the chlorophyll fluoresces brightly. A molecule that cannot intersystem cross can not go to the. This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings.
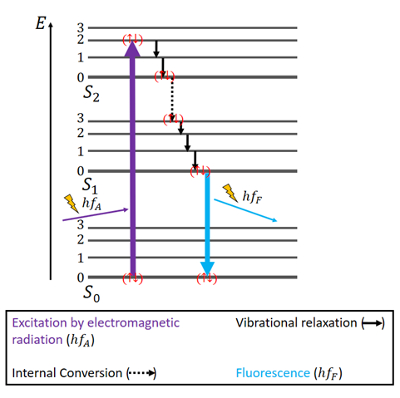
Fluorescence is the property of some atoms and molecules to absorb light at a particular wavelength and to subsequently emit light of longer wavelength after a brief interval termed the fluorescence lifetime. But in some molecules the spins of the excited electrons can be switched to a triplet state in a process called inter system crossing. When an electron has been excited to a higher energy state it can then drop back to the original level re-emitting the light as fluorescence.
Fluorescence a type of luminescence occurs in gas liquid or solid chemical systems. Fluorescence is the property of some atoms and molecules to absorb light at a particular wavelength and to subsequently emit light of longer wavelength after a brief interval termed the fluorescence lifetime. 3 Electron unstable returns to ground state and releases energy fluorescence.
Fluorescence is a cyclical phenomenon when electrons of a fluorescently active compound are repeatedly excited to return to their ground energetic state upon emitting photons of. View the full answer. Which of the following describes the initial steps in the process.
The initial excitation is usually caused by absorption of energy from incident radiation or particles such as X-rays or electrons. The process of emission follows extremely rapidly commonly in the order of nanoseconds and is known as fluorescence. The radiative de-excitation process can be described as a monomolecular process.
Epinephrine is a protein hormone found in many animals. Fluorescence is brought about by absorption of photons in the singlet ground state promoted to a singlet excited state. 2 Electron rises to a higher energy level excited state.
100 Fill in the words to describe the process of fluorescence. Fluorochromes are essentially dyes which accept light energy eg from a laser at a given wavelength and re-emit it at a longer wavelength. 4 But some energy lost so released at.
The spin of the electron is still paired with the ground state electron unlike phosphorescence. These two processes are called excitation and emission. A fluorescence example would be if a 3s electron of a vaporized sodium atom is excited to the 3p state by absorption of a radiation at wavelength 5896 and 5890 nm.
- Energy state of an electron is raised. Quartz is a material that undergoes this process. Epinephrine stimulates a signaling pathway that results in the breakdown of glycogen to glucose in the liver cells.
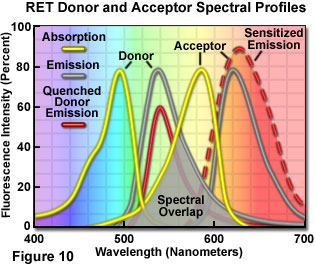
Fluorescence De-excitation can occur via a radiative decay ie. Fluorescence is the result of a three-stage process that occurs in certain molecules generally polyaromatic hydrocarbons or heterocycles called fluorophores or fluorescent dyes Figure 1. A fluorescent probe is a fluorophore designed to respond to a specific stimulus or to localize within a specific region of a biological specimen.
Fluorescence is the process in which a molecule excited by the absorption of radiation emits a photon while undergoing a transition from an excited singlet electronic state to a lower state of the same spin multiplicity eg a singlet singlet transition. Excited Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or. A substance is said to be fluorescent when it absorbs the energy of invisible shorter wavelength radiation such as UV light and emits longer wavelength radiation of visible light such as green or red light.
Fluorescence is the phenomenon of absorption of electromagnetic radiation typically from ultraviolet or visible light by a molecule and the subsequent emission of a photon of a lower energy smaller frequency longer wavelength. Fluorescence microscopy is a type of light microscope that works on the principle of fluorescence. A transient excited lifetime with some loss of energy.
Return of the fluorophore to its ground state. Therefore all observed fluorescence normally. Fluorescence emission of electromagnetic radiation usually visible light caused by excitationof atomsin a material which then reemit almost immediately within about 108seconds.
The cyclical fluorescence process can be summarized as. Fluorescence occurs when a substance has absorbed light and later emits that light. Describe the observed fluorescent activity of each test tube of the 4 under the UV light in the test tube and on the filter paper eg.
- Molecule absorb energy from a photon of light. Click again to see term. Tap card to see definition.
The process of phosphorescence occurs in a manner similar to fluorescence but with a much longer excited state lifetime. Fluorescence is the process by which the molecule that has singlet spin multiplicity in an excited state loses energy typically back to its ground state with emission of light it is characterized by k fl which is typically on the time scale of 10 6 -10 9 sec -1. 1 Fluorescent molecule absorbs light of a specific wavelength.
Fluorescence can occur in gaseous liquid and solid chemical systems. A medication enters the target cell and inhibits an enzyme that normally synthesizes a second messenger. Click card to see definition.
Not yet answered Points possible. These electrons lose energy until they are in the triplet ground state.
What Are Fluorescence And Phosphorescence Chemistryviews
Fluorescence Excitation Emission Emission Spectrums Olympus Ls

Fluorescence Excitation Emission Emission Spectrums Olympus Ls

What Is Fluorescence Anisotropy Or Fluorescence Polarization Horiba
No comments for "Best Describes the Process of Fluorescence"
Post a Comment